
In order to maintain a reasonable cost for large scale structures such as airframes, offshore structures, nuclear plants etc., it is generally accepted that improved methods for structural integrity and durability assessment are required. Structural Health Monitoring (SDHM) had emerged as an active area of research for fatigue life and damage accumulation prognostics.
This journal is a member of the Committee on PublicationEthics (COPE).
Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2023): 2.4; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2023): 0.579; RG Journal Impact (average over last three years); Engineering Index (Compendex); Applied Mechanics Reviews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts: Aerospace and High Technology, Materials Sciences & Engineering, and Computer & Information Systems Abstracts Database; INSPEC Databases; Mechanics; Science Navigator; Portico, etc...
 Refers to the articles published on the journal within the last three years that have gained the most viewing times to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
Refers to the articles published on the journal within the last three years that have gained the most viewing times to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
 Refers to articles published on the journal since 2020 that have received the most frequent citation to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
Refers to articles published on the journal since 2020 that have received the most frequent citation to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 363-380, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.042388
Abstract Concrete materials and structures are extensively used in transformation infrastructure and they usually bear cracks during their long-term operation. Detecting cracks using deep-learning algorithms like YOLOv3 (You Only Look Once version 3) is a new trend to pursue intelligent detection of concrete surface cracks. YOLOv3 is a typical deep-learning algorithm used for object detection. Owing to its generality, YOLOv3 lacks specific efficiency and accuracy in identifying concrete surface cracks. An improved algorithm based on YOLOv3, specialized in the rapid and accurate identification of concrete surface cracks is worthy of investigation. This study proposes a tailored… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 395-408, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.049366
Abstract Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is the most flowable concrete type that exerts high pressure on formwork. SCC is the most commonly used concrete globally for construction applications due to its cost-effectiveness. However, to make a formwork resist the exerted lateral pressure of SCC, it is required to have a suitable design for formwork. This paper presents a novel approach on how could create and prepare the Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) optics using as a sensor to measure lateral pressure and temperature of SCC. To ensure the FBG sensor works properly a validated methodology is conducted. In More >
Graphic Abstract

 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 409-423, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.048597
Abstract In this paper, recycled carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) mixture (CFRP-M, including recycled carbon fiber and powder) and refined recycled CFRP fiber (CFRP-F, mostly recycled carbon fiber) were added to cement to study the influence of addition on the flexural strength, compressive strength, and fluidity of cement-based materials. The recycled CFRP were prepared by mechanically processing the prepreg scraps generated during the manufacture of CFRP products. For comparison, commercial carbon fiber powder was also added in cement and the performance was compared to that of addition of recycled CFRP. The hydration products and strengthening mechanism… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 425-444, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.046584
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring and Rapid Evaluation of Infrastructures)
Abstract Due to the lack of a quantitative basis for the inspection, evaluation, and identification of existing transmission tower foundations, a new fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method is proposed to assess the reliability of transmission tower foundation bearing capacity. This method is based on the reliability analysis of the transmission tower foundation bearing capacity by analyzing the sensitivity of degradation of detection indexes on the reliability of transmission tower foundation bearing capacity, the weighting coefficient matrix is established about the influencing factors in the evaluation model. Through the correlation analysis between the bearing capacity degradation of the More >
Graphic Abstract
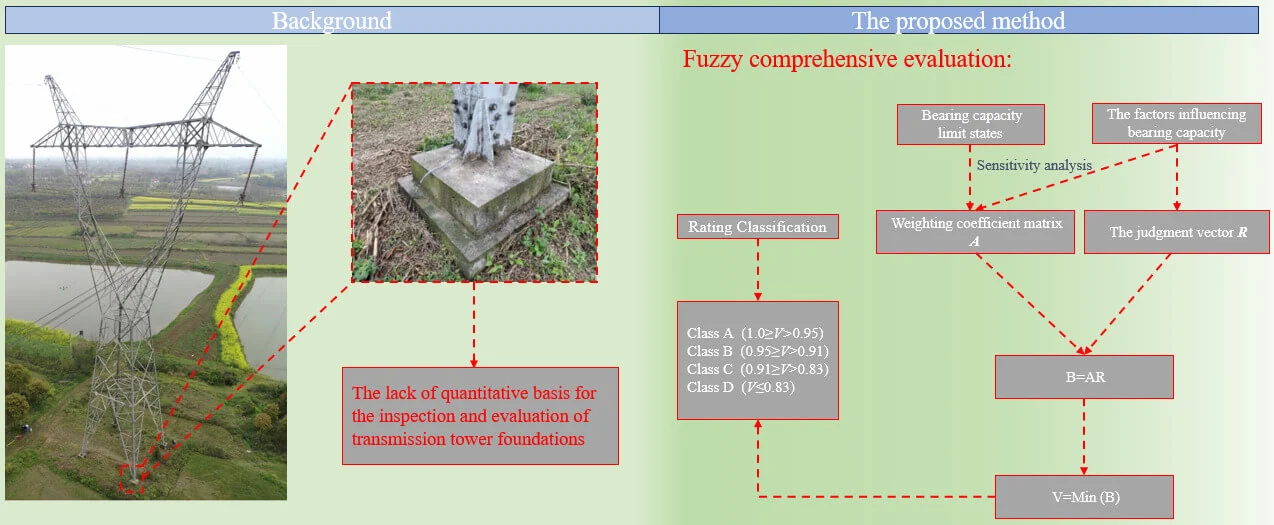
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 445-463, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.049298
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sensing Data Based Structural Health Monitoring in Engineering)
Abstract The vibration signals of rolling bearings exhibit nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics under the influence of noise. In intelligent fault diagnosis, unprocessed signals will lead to weak fault characteristics and low diagnostic accuracy. To solve the above problem, a fault diagnosis method based on parameter optimization feature mode decomposition and improved deep belief networks is proposed. The feature mode decomposition is used to decompose the vibration signals. The parameter adaptation of feature mode decomposition is implemented by improved whale optimization algorithm including Levy flight strategy and adaptive weight. The selection of activation function and parameters is More >
Graphic Abstract
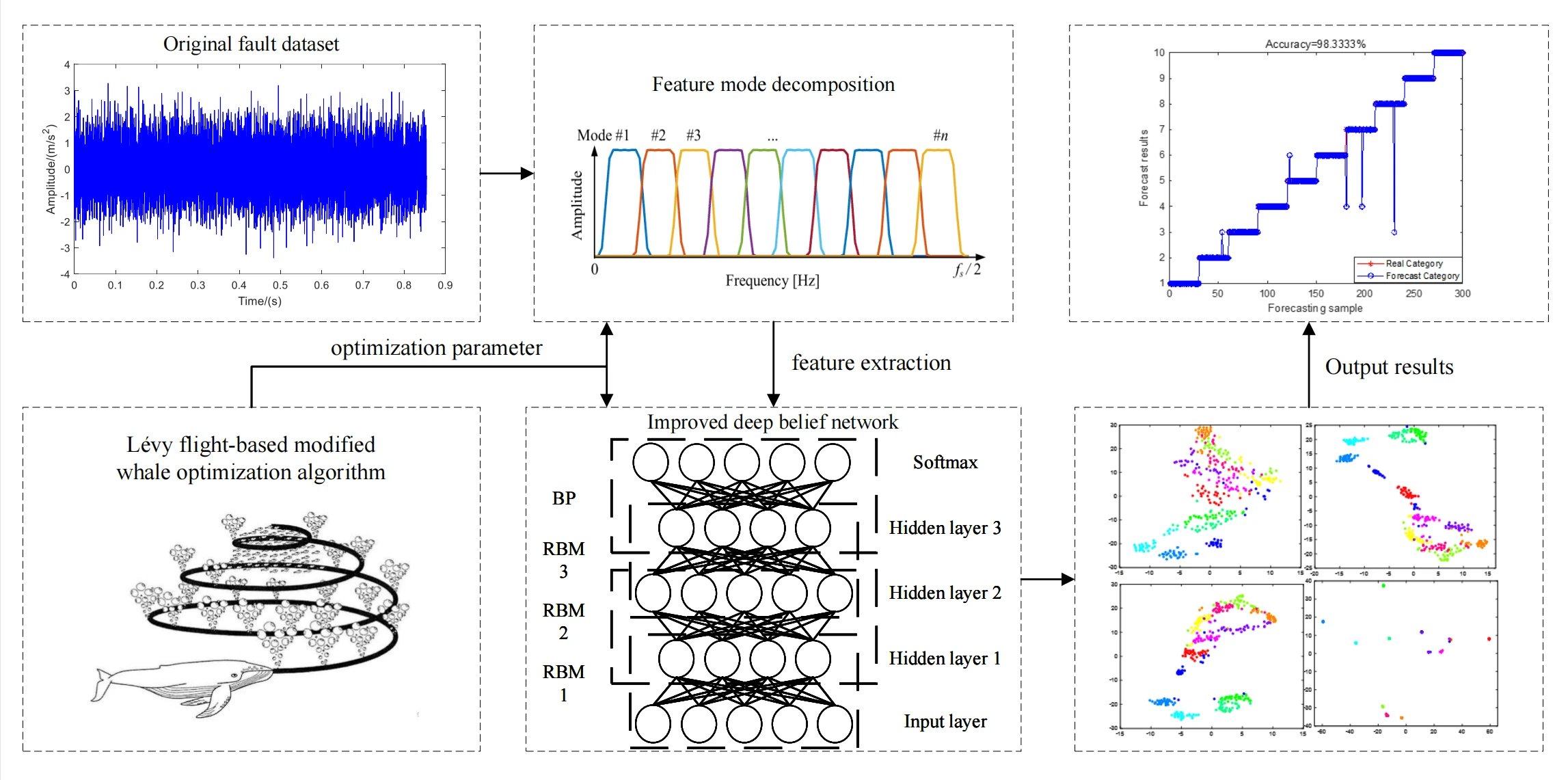
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 465-483, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.048705
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sensing Data Based Structural Health Monitoring in Engineering)
Abstract In this paper, an intelligent damage detection approach is proposed for steel-concrete composite beams based on deep learning and wavelet analysis. To demonstrate the feasibility of this approach, first, following the guidelines provided by relevant standards, steel-concrete composite beams are designed, and six different damage incidents are established. Second, a steel ball is used for free-fall excitation on the surface of the steel-concrete composite beams and a low-temperature-sensitive quasi-distributed long-gauge fiber Bragg grating (FBG) strain sensor is used to obtain the strain signals of the steel-concrete composite beams with different damage types. To reduce the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 485-503, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.049698
Abstract This study addresses the issue of inaccurate single damage fingerprint recognition during the process of bridge damage identification. To improve accuracy, the proposed approach involves fusing displacement mode difference and curvature mode difference data for single damage identification, and curvature mode difference and displacement mode wavelet coefficient difference data for two damage identification. The methodology begins by establishing a finite element model of the cable-stayed bridge and obtaining the original damage fingerprints, displacement modes, curvature modes, and wavelet coefficient differences of displacement modes through modal analysis. A fusion program based on the D-S evidence theory… More >
Graphic Abstract
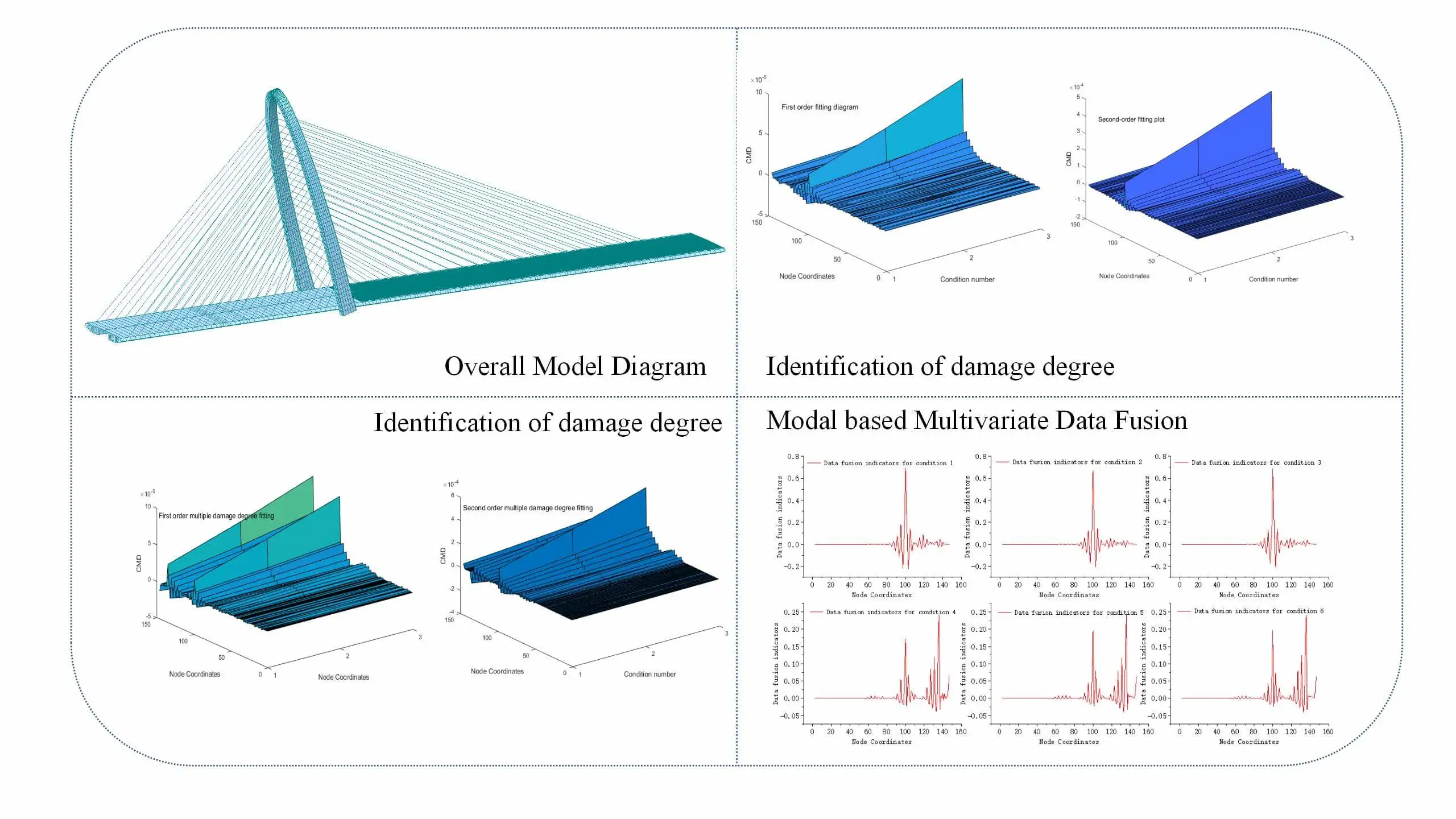
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.18, No.4, pp. 505-524, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2024.049363
Abstract In this study, we assessed the impact of substituting natural fine aggregates with municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash (MSWI-BA) in steel fiber (SF)-reinforced concrete on its compressive properties post high-temperature exposure. The concrete specimens incorporating MSWI-BA as the fine aggregate and SFs for reinforcement underwent uniaxial compression tests after exposure to high temperatures. Through the tests, we investigated the impact of high-temperature exposure on mechanical properties, such as mass loss rate, stress-strain full curve, compressive strength, peak strain, elastic modulus, and so on, over different thermostatic durations. The analysis revealed that with the increasing… More >